What is "this" keyword in JavaScript?
this is a keyword that's used a lot in Object Oriented Programming. In traditional Object Oriented Programming languages, this points to the object. But in JavaScript, the value of this changes depending on how we call a function, so this can be quite confusing for JavaScript beginners.
So basically what is this keyword?
This keyword = It's a special identifier keyword that's automatically defined in the scope of every function. which links to the object in which the function operates.
Taking Deep Dive with This
thisis not a compile time binding it is a run time binding. which dynamically refers to different things in different contexts.thisbinding has nothing to do with where a function is declared but instead has everything to do with the manner in which the function is called, also called as call-site ( The location in code where a function is called === Call Site ). So all the game ofthiskeyword is based on where the call-site is present because the reference ofthiskeyword is depend on call site.When a function is invoked, an activation record(otherwise known as an execution context) is created. This record contains information about where the function was called from(call-site), how the function was invoked, what parameters were passed, etc.. one of the properties of this record is the
this reference, which will be used for duration of function's execution.
So now we know what is this keyword and which parameters it depends on.
Now we look on the values it works with :
It can take up to four different values:
- window
- The object
- The
thisvalue in its immediate context. - The listening element.
1. window Object
- By default
thisrefers to global object The meaning of
globalobject is the default state for the execution context for an execution isglobal, which means if a code is being executed as part of a simple function call thenthisrefers toglobalobject.- In Browser Environment =
windowobject is a global object . - In Node.js Environment = Special object
globalwill be the value of this.
- In Browser Environment =
thisin global scope/simple_function/IIFE === Points to the window object.
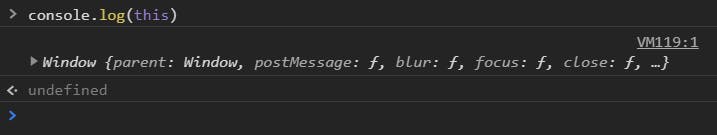
Case 1: this in global context.
console.log(this) //window
Case 2: this in simple function.
Case 3: this in IIFE(Immediately invoked Function).
Case 4: this in strict mode.
If strict mode is enabled for any function then the value of this will be undefined as in strict mode, global object refers to undefined in the place of window object.
Note: You are working with Web-Pack then you will also see undefined as it doesn't allow us to access the global object.
2. The Object
Case 1: "this" in Constructor Function.
this in Constructor Function === Points to Newly Created Instance.
When a function is invoked with “new” keyword then the function is known as constructor function and returns a new instance. In such cases, the value of this refers to newly created instance.
Case 2: this in Object's Method.
this in Object's Method === Points to invoker object (Parent object)
In JavaScript, property of an object can be a method or a simple value. When an Object’s method is invoked then this refers to the object which contains the method being invoked.
One frustrating thing for beginners to understand is this – this always point to window, even if the simple function is used in a method.
When it is being called as a simple function call then this refers to global object and when the same definition is invoked as an object’s method then this refers to the parent object. So the value of this depends on how a method is being invoked as well.
3. The this value in its immediate context
thisin Arrow functions === Points to samethisvalue in surrounding scope.
Case 1 : this in Arrow Functions.
this in an arrow function always points to the same this value in the surrounding scope.
In the example below, the this value within firstName is the same value as this in name . Since the this value in name is the Person, this within the arrow function also points back to the Person.
When arrow functions are used to create functions in methods, this will point back to the object.
If you use the arrow function to create simple functions in a global context, this points to window because window is the this value of the surrounding scope.
4. The Listing Element
thisin listing element === Points to the listening element
Case 1 : this in listening element.
When this is used in an event listener, this points back to the button
Remember, when you write event listeners with arrow functions, you can still get the listening element with event.currentTarget, even though this points to something else.
Binding Rules for this Keyword!!
- Default Binding
- Implicit Binding
- Explicit Binding
newBinding- Lexical binding
windowbinding
1. Default Binding :
Default binding is nothing but a normal calling method of function.
2. Implicit Binding :
In Implicit binding, this keyword will bind with the object which stands before the dot operator.
Implicit binding occurs when dot notation is used to invoke function.
In Implicit binding, we use the object to call the functions with the dot operator.
In Below Code :
obj is the this for the foo() call
3. Explicit Binding :
In Explicit Binding, we can force a function call to use a particular object for this binding, without putting a property function reference on the object. So we can explicitly say to a function what object it should use for this — using functions such as call(), apply() and bind().
Explicit binding of this occurs when .call(), .apply() or .bind() are used on a function.
We call these explicit because we can explicitly passing in a this content to call() or apply()
Case 1: this with call(), apply() methods.
A function in JavaScript is also a special type of object. Every function has call(), bind() and apply() methods. These methods can be used to set custom value of this to the execution context of function.
call() : The call method calls/invoke/activate a another function with a given this value and arguments provided individually.
Syntax for call() function: sampleFunction.call(thisContext, param1, param2, ... )
The only difference between call and apply method is the way argument is passed. In case of apply method, second argument is an array of arguments where in case of call method, arguments are passed individually.
Syntax for apply() function: sampleFunction.apply(thisContext, [param1, param2, ...])
Case 2: this with bind() Method :
bind() method is the exact same as call() method but instead of immediately invoking the function, it will return a new function that we can invoke at a later time.
bind() provides two opportunities to call a function
Case 3 : this with hard binding.
Hard Binding: When binding is both explicit and strong.
our showDetails.call(fullname) is an explicit binding and when we put this statement in a function then it is called as strong binding and after the strong binding the value of this is not overridden.
even in window object its refer to the object fullName
4. new binding :
new binding is nothing but we use 'new' keyword, so when we invoke a function with this 'new' keyword, under the hood, the JavaScript interpreter will create a brand new object for us and call it this. Otherwise call as "Constructor Call".
5. Lexical Binding
We use Arrow function to demonstrate lexical binding, as arrow function don't have its own this so Instead this is determined lexically.
lexical binding of an arrow function cannot be overridden.
6. window Binding
Explain with an Example :
Summary
Short overview of values that this will be working on:
thisin constructor functions andthisdirectly in a method point to the object itself.thisin a global context andthisin a simple function point towindow.thisin an arrow function always takes up the value ofthisin its surrounding scope.thisin an event listener points to the listening element.
Short overview of binding rules that are used with 'this' :
- Look where the function was invoked.
- If there is an object on left side of dot operator, then
thisrefer to this object (Implicit Binding) - If the function invoked with
call,apply, orbind? thenthisexplicitly refer to an object.(explicit Binding) - If the function invoked using the
newkeyword? then thethiskeyword is refer to a newly created object that was created by JavaScript interpreter. (newBinding) - If
thisinside of an arrow function? then it is refer lexically in the enclosing (parent) scope. (lexical Binding) - If we are in strict mode? then
thiskeyword isundefined. - if we are in global scope or in simple function scope? then
thiskeyword is refer to awindowobject.

